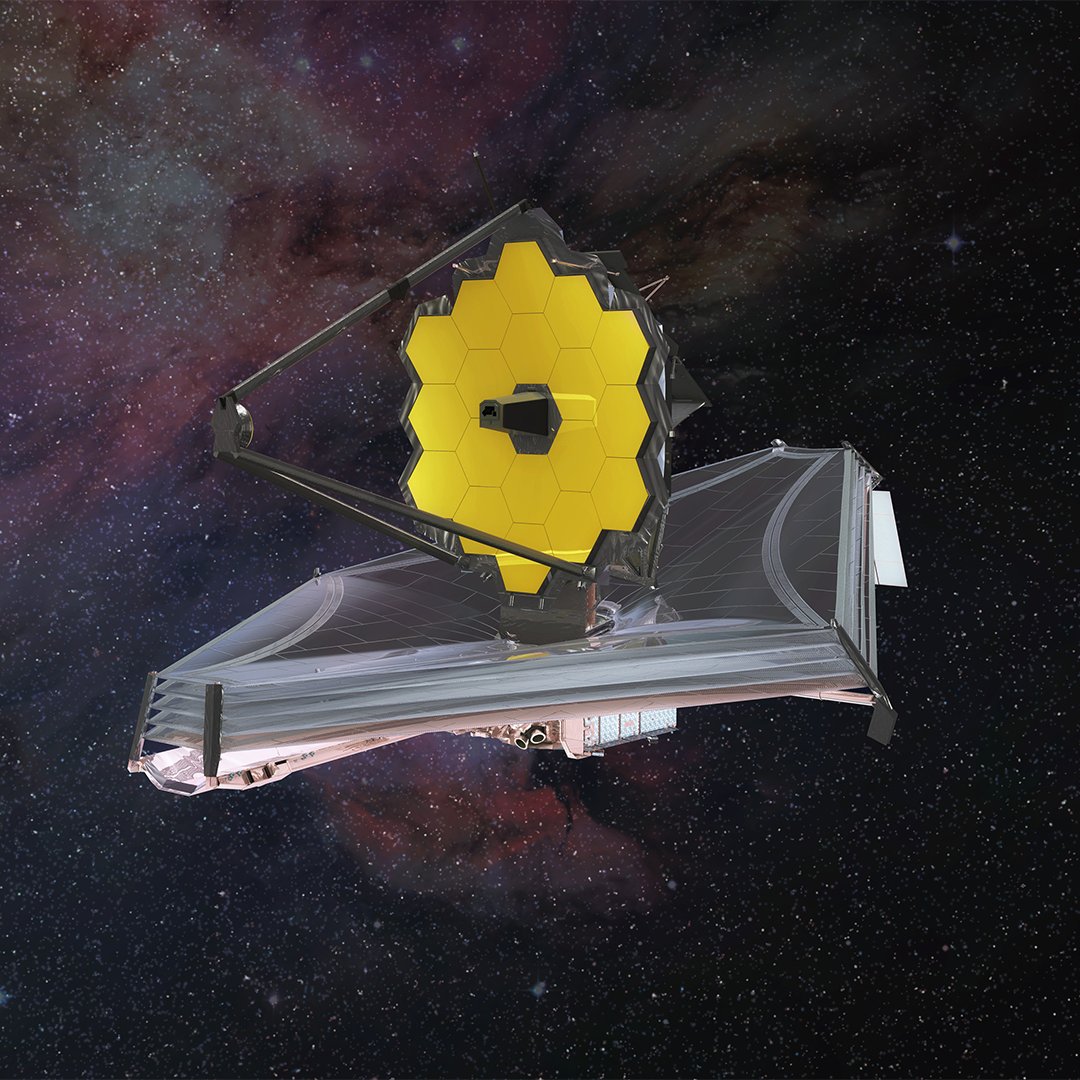
 The James Webb Space Telescope The James Webb Space Telescope
Uses 15 Teledyne H2RG 2048×2048 pixel infrared detectors Teledyne supplied 63 million IR pixels for three of JWST’s instruments: Near Infrared Camera (NIRCam), Near Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec), and the Fine Guidance Sensor (FGS) Credit: Northrup Grumman
|
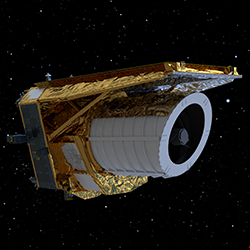 Euclid Space Telescope Euclid Space Telescope Uses 16 Teledyne H2RG 2048×2048 pixel infrared detectors for the Near Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP), which uses a 4×4 matrix of 2040×2040, 18 µm pixel detectors. Also includes 36 Teledyne CCD273-84 visible sensors in a 6x6 mosaic of 4096×4132m, 12 µm pixel for a total of about 600 megapixels.
Credit: ESA
|
 Plato (PLAnetary Transits and Oscillations of stars) Plato (PLAnetary Transits and Oscillations of stars) Uses 26 cameras to find and study terrestrial exoplanets in orbits in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars. Each of the 26 cameras uses four Teledyne visible CCDs; each CCD has 4510x4510 pixels (18 µm pitch). Each camera has more than 81 million pixels, and there are a total of more than 2 billion CCD pixels in the 26 cameras of the PLATO mission.
Credit: ESA/ATG medialab
|
 Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope The infrared sensor chip assembly (SCA) developed for Roman is the H4RG-10, 4,096×4,096 pixels, and each pixel is 10 by 10 microns in size. (A human hair is about 100 microns wide.) 18 H4RG-10 SCAs are in the focal plane mosaic of Roman, totalling over 300 million pixels. This is by far the largest infrared focal plane ever made, for space or ground-based facilities. In addition to the infrared arrays, Teledyne also produced three visible light CCD311-20 detectors that will be used in the coronograph instrument of the Roman Space Telescope. Credit: NASA
|
